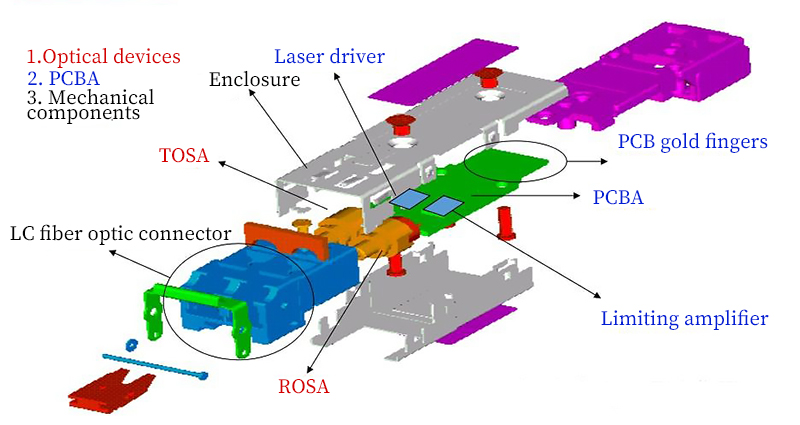
What is a Laser Module?
As a modular device that integrates lasers, related optical components, circuits, and control units, the laser module provides a stable and efficient laser light source for a variety of applications. Its core functions involve the generation, modulation, transmission, and focusing of laser light to meet the needs of different fields. In this blog, ATO will delve into all aspects of laser modules, including their unique structure, operating principles, diverse types, and applications across various industries.
Basics of Laser Modules
The laser module serves as the light source within a laser unit, akin to the bulb inside a lamp, and is a kind of passive component. Inside the laser module are various laser diodes and optical devices/crystals, with the laser diode functioning as the light source when powered. Laser modules are characterized by their compact size, simple structure, ease of installation, and ability to form effective spot patterns for project production as required.
Early laser modules utilized gas lasers tubes filled with specific gases (such as argon, mixed gases, or helium-neon) to produce laser beams through high-power gas excitation. This technology evolved to DPSS (Diode Pumped Solid State), where DPSS lasers use high-power infrared sources to focus light onto specific crystals (like Nd:YAG) to produce lasers of various wavelengths. In recent years, diode laser technology has become the standard for laser modules in laser shows. This technology generates laser light by controlling the current to the laser diode and is common in the laser show industry due to its reliability and long lifespan.
Structure of Laser Modules
The components of a laser module primarily include laser diodes, drive circuits, optical elements, cooling systems, and enclosures. These components together form a complete laser system designed to emit laser beams or patterns of fixed wavelengths, mainly used for illumination or atmosphere enhancement.
- Laser Diode: The main component for emitting laser light; different types of laser diodes emit different laser wavelengths.
- Drive Circuit: Provides a stable current to the laser diode for normal operation.
- Optical Elements: Include lenses that can alter the shape of the spot, used to adjust the shape and direction of the beam.
- Cooling System: Necessary to dissipate heat produced by the laser diode during operation, maintaining stability and extending lifespan.
- Enclosure: Protects the internal components of the laser module from external environmental influences.
Types of Laser Modules
Within modern laser modules, linear and scanning designs are two common types:
Linear line laser modules project the laser beam directly as a straight line and output it parallelly. They are capable of projecting the laser beam in a straight line to form a clear line with good directionality and visibility, though the line laser spot may be relatively thick. These modules typically have a simpler structure, making them easy to install and use within equipment.
Scanning line laser modules produce a line through the use of cylindrical lenses, wave mirrors, Powell lenses, etc., with adjustable line laser size. Scanning line laser modules can adjust the laser spot size as needed, adapting to various scanning ranges and achieving the projection of fine lines of different lengths. These modules can scan over a larger area, suitable for applications requiring extensive coverage.
Comparative Analysis
Linear modules project horizontally, while scanning modules project at a certain emission angle. Linear modules have a smaller coverage area, while scanning modules have a larger, adjustable coverage area. Linear modules have less flexibility but are well-suited for gap scanning, whereas scanning modules offer high flexibility and control, suitable for most scanning detection applications.
Applications of Laser Modules
Optical Communication
Laser modules are widely used in the field of optical communication, mainly in fiber optic communication, wireless communication, and satellite communication. Laser modules can transmit data in the form of optical signals, characterized by fast transmission speeds, large bandwidth, and strong anti-interference capabilities, playing a crucial role in modern communication.
Medical Aesthetics
The application of laser modules in the medical aesthetics field is also extensive, used primarily for skin beauty, laser surgery, and viewing internal organs. Laser modules can achieve effects such as spot and wrinkle removal and laser treatment through specific wavelengths of laser light, revolutionizing the medical aesthetics industry.
Surveying Instruments
Laser modules can also be used in surveying instruments, such as radar ranging and laser scanning. The high precision and non-contact features of laser modules make them outstanding in surveying instruments.
Industrial Control
The application of laser modules in the field of industrial control is also extensive, such as in laser cutting, laser welding, and laser marking. Laser modules enable efficient and precise processing, playing an important role in industrial production.
As a one-stop shop for industrial equipment, the ATO online store offers a wide range of high-quality laser modules in various specifications. Should you have any requirements, our competitively priced and reliable products are poised to be your optimal solution.
The laser module, as a device that integrates multiple advanced technologies, has transformed the paradigm of today’s technology-driven world. Its precision, versatility, and innovation have made it an indispensable tool across all industries. At ATO, we are committed to providing you with the best laser modules on the market. Don’t miss the opportunity to elevate your project to new heights. Visit our online store at ato.com and experience the power of precision and innovation now!