What are the Types of Rectifier?
In the world of power electronics, there are many different types of rectifiers, each with their own unique uses and benefits. At One-stop Industrial AutomationShop, we are proud to offer a wide range of different types of rectifiers to meet the needs of a variety of customers. Whether you're looking for a simple diode rectifier or need a more advanced SCR rectifier, we have it all. This blog will delve into the different types of rectifiers, from the simple to the complex, to fully demonstrate the diversity of rectifier types and their importance in different application scenarios.
Types of Rectifier
Categorized by Control Capability:
Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR): A silicon controlled rectifier is a circuit that utilizes silicon controlled elements to achieve rectification. SCR is a four-layer semiconductor device with three PN junctions. By controlling its triggering angle, the output voltage can be adjusted, which has a high power capacity and can withstand high current and high voltage. It can realize stepless voltage regulation and flexible control. However, it requires a trigger circuit, and the control is more complicated. Widely used in industrial fields, such as motor speed regulation, electroplating, electrolysis and so on.
Uncontrollable Rectifiers: The output voltage or current of these rectifiers is fixed and cannot be adjusted by external control signals. Uncontrollable rectifier structure is simple, low cost, in some of the output requirements are not high occasions more applications.
Categorized by Circuit Structure:
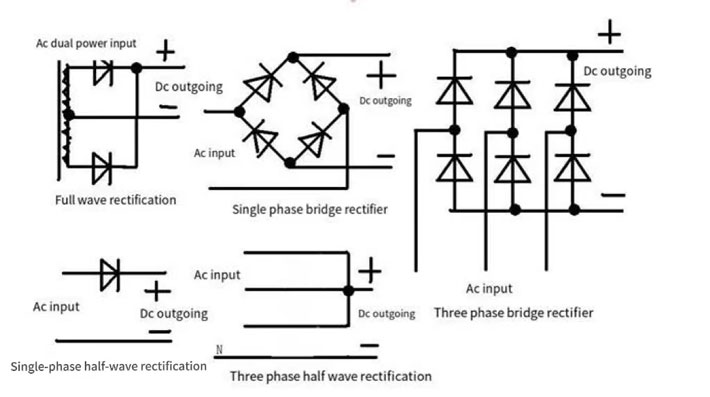
Single-Phase Rectifier: Single-phase rectifier is a single-phase alternating current through a single diode Bridge rectifier bridge for rectification, the output is a half-wave DC. Including single-phase half-wave rectifier and single-phase full-wave rectifier. Single-phase half-wave rectifier uses a diode to convert one half-cycle of AC to DC; single-phase full-wave rectifier uses two diodes or a bridge rectifier circuit to convert both half-cycles of AC to DC. Compared with three-phase rectifiers, single-phase rectifiers are inexpensive and simple in structure, but the output DC voltage is low and poorly regulated, making them suitable only for low-power electronic devices.

Three-Phase Rectifier: Three-phase rectifier, also known as three-phase full-wave rectifier, usually consists of three scrupulous phase transformers, one end of each transformer is connected to the three-phase power supply, the other end of the diode bridge rectifier rectifier through a single diode Bridge rectifier bridge to rectify the output of the full-wave DC power. These include three-phase half-wave rectifiers and three-phase full-wave rectifiers. Compared with single-phase rectifiers, three-phase rectifiers output high DC voltage, good regulation and smooth current, which is suitable for large motors, control systems and power electronic equipment.
Categorized by Configuration:
Half-Wave Rectifiers: Half-wave rectifiers are one of the simplest types of rectifiers. It consists of a diode, when the positive half of the alternating current comes, the diode conducts and the current passes through the load; when the negative half of the alternating current comes, the diode cuts off and the current cannot pass through the load. Therefore, the half-wave rectifier can only conduct in half a cycle of the alternating current, the output DC is pulsating. The structure of the half-wave rectifier is simple and low cost. However, the output voltage pulsation is large and the efficiency is low. Applicable to some of the power requirements of the occasion is not high, such as small electronic equipment, toys and so on.
Full-Wave Rectifier: Full-wave rectifier is usually composed of two diodes, or use a center-tapped transformer and four diodes composed of a bridge rectifier circuit. In the positive and negative half-cycle of the alternating current, there is a current through the load, thus realizing the full-wave rectifier. It is characterized by smaller output voltage pulsations and higher efficiency. However, it requires the use of a center-tapped transformer, which increases the cost and size. It is widely used in various electronic devices and power supplies.
Categorized by Application:
Precision Rectifiers: Precision rectifiers are used to achieve accurate rectification of input AC signals through the use of operational amplifiers and diodes. In a precision rectifier circuit, an operational amplifier is used to compensate for the forward voltage drop of the diode, thus realizing the precise rectification of the signal, so that even very weak AC signals can be accurately converted into DC signals. Precision rectifiers are usually used for signal processing, demanding occasions, such as measurement equipment, sensor signal conditioning, etc.
Capacitive Coupled Rectifier: Capacitive coupled utilizes the charging and discharging characteristics of a capacitor to transmit an AC signal while blocking the DC component. In a capacitively coupled rectifier, the capacitor allows the AC signal to pass through while blocking the DC component, thus realizing rectification. This method is commonly used for signal isolation and interstage coupling, especially in applications where the integrity of the signal waveform needs to be maintained, such as audio signal processing.
How to Select Rectifier Type
When selecting a rectifier, the following factors need to be considered:
- Input voltage and current: Determine the input voltage and current range of the rectifier according to the actual application scenario.
- Output voltage and current: Determine the output voltage and current size of the rectifier according to the demand of the load.
- Efficiency and power loss: Select rectifiers with high efficiency and low power loss to reduce energy consumption and heat generation.
- Reliability and stability: Select rectifiers with high reliability and good stability to ensure the normal operation of the equipment.
- Cost and volume: according to the budget and space constraints, choose the rectifier with low cost and small volume.
Different types of rectifiers have their own advantages in different application scenarios. For example, half-wave rectifiers and full-wave rectifiers may be a more appropriate choice for low-power applications; silicon controlled rectifiers and diode rectifier modules are more suitable for high-power applications.
Understanding the different types and characteristics of rectifiers will help you to choose the right rectifier for your needs. If you are interested in a specific type of rectifier or other related issues, you can click into the ATO Industrial Automation Shop to contact us!

