Types of Vacuum Gauges
A vacuum gauge is an instrument used to measure the degree of vacuum or air pressure. Generally, the measurement of air pressure is based on the changes in a certain physical effect under different air pressures. Widely used in scientific research and industrial production. The main component of a vacuum gauge is a hot cathode, and the heat emitted electrons generated during its operation ionize the gas. This ion flow is proportional to the number density of gas molecules. When all other parameters, including temperature, are constant, the size of the ion flow is proportional to the air pressure, and the air pressure value can be obtained by measuring the ion flow. The hot cathode ion gauge is mainly composed of three electrodes, namely cathode, gate, and collector.
According to the different physical mechanisms utilized in the measurement principle of vacuum gauges, the main types of vacuum can be classified into three categories: vacuum gauges that utilize mechanical properties, those that utilize gas dynamics, and those that utilize charged particle effects. Typical vacuum gauges that utilize mechanical properties include Bourdon gauges and thin-film capacitance gauges; Typical vacuum gauges that utilize gas mechanical effects include Pirani resistance gauges and thermocouple gauges; Typical vacuum gauges that utilize charged particle effects include hot cathode ionization gauges and cold cathode ionization gauges.
Vacuum Gauge with Mechanical Properties
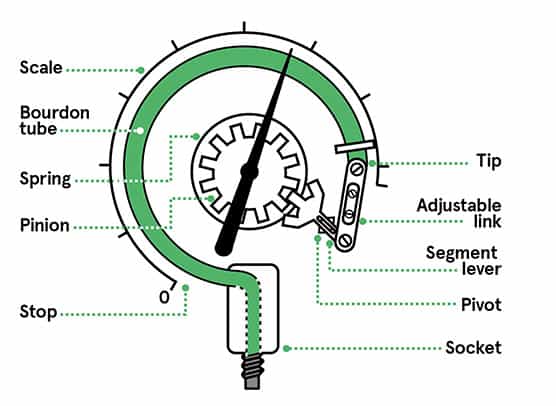
Bourdon Gauges
Copper pipes will stretch under different gas pressures, which will drive the lever and gear to rotate, so that the pointer can indicate the corresponding pressure value on different scales. The measurement range of this gauge is generally between 100Pa and 1atm. As shown in the figure on the right, under different pressures, the metal diaphragm will undergo deformation of different scales due to different forces, resulting in changes in capacitance between the metal diaphragm and the electrode. By measuring the change in capacitance, the change in air pressure on the metal diaphragm can be determined. The measurement range of this gauge generally spans four orders of magnitude, such as 0.01Pa to 100Pa, 0.1Pa to 1000Pa, etc.
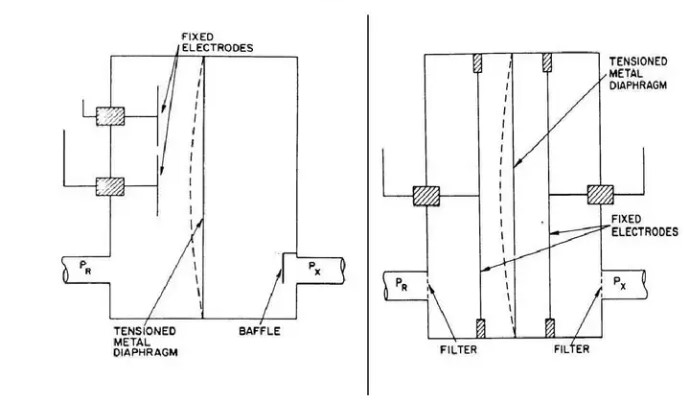
Thin-film Capacitance Gauges
Thin film capacitance gauge is a pressure sensor that uses vacuum pressure to deform the diaphragm. The deformation is proportional to the pressure, and the vacuum degree is measured by measuring the deformation of the ceramic diaphragm under different pressures. This vacuum gauge can provide stable and reliable high-precision pressure measurement in harsh and corrosive environments. It has fast preheating and recovery time, excellent long-term stability, reproducibility, and repeatability, and reduced sensitivity to changes in environmental conditions. Generally used for high demand, accurate and fast measurements, such as etching, semiconductors, etc.
Vacuum gauge for gas mechanical effects
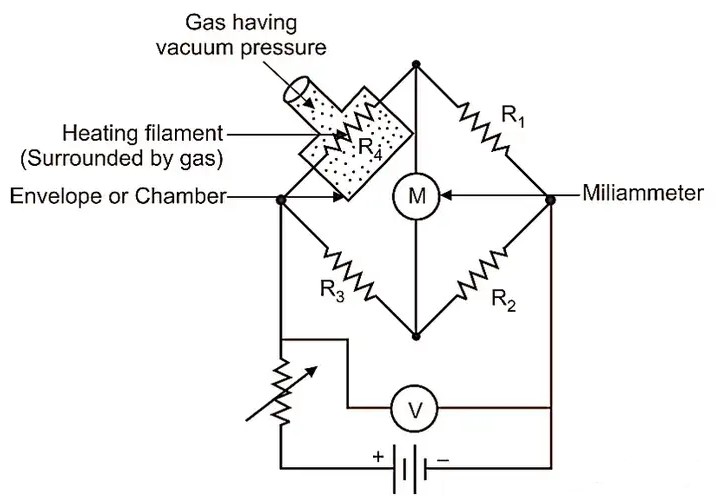
Pirani Resistance Gauges
The working principle of a Pirani vacuum gauge is that the thermal conductivity of a gas decreases with decreasing pressure. The construction of Pirani vacuum gauge: Pirani vacuum gauge is also a thermal conductivity measuring instrument, similar to thermocouple vacuum gauge. The Pirani vacuum gauge consists of a heating wire enclosed indoors. The heating element or filament is a platinum wire that forms one arm (resistor) of a Wheatstone bridge. The heating filament is heated by a constant current. Therefore, the temperature of the heating filament will increase. For a given magnitude of current, the temperature of the heating wire depends on the rate of heat dissipation to the surrounding medium (i.e. gas) through conduction and convection. After heating, place or connect the heating wire to a vacuum or low-pressure surrounding gas medium. Now, due to the heating wire being surrounded by vacuum or low-pressure gas, the thermal conductivity of the heating wire (i.e. the ability of the heating wire to dissipate heat to the surrounding medium) will also decrease. In this case, the heating wire will be hotter. The change in heating wire temperature can cause a change in wire resistance, which can be measured by a Wheatstone bridge.It is generally used for pre pressure measurement of various high vacuum pumps, such as photovoltaic, coating, plasma industries, etc., and is also used for various low and medium vacuum measurements.
Thermocouple Gauge
A thermocouple gauge that uses the principle that the potential of a thermocouple is related to the temperature of the heating element, and the temperature of the element is related to the thermal conduction of the gas to measure vacuum degree.
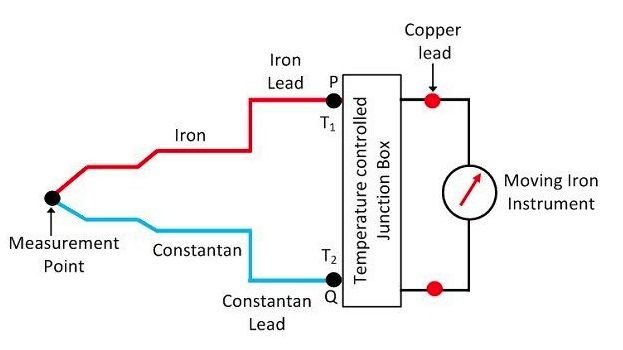
The basic principle of thermocouple temperature measurement is that two conductors with different compositions form a closed circuit. When there is a temperature gradient at both ends, current will flow through the circuit, and there will be an electromotive force - thermoelectric potential - between the two ends. Two homogeneous conductors with different compositions are thermoelectric electrodes, with the higher temperature end as the working end and the lower temperature end as the free end, which is usually at a constant temperature. Create a thermocouple calibration table based on the functional relationship between thermoelectric potential and temperature; The calibration table is obtained under the condition of a free end temperature of 0 ℃, and different thermocouples have different calibration tables. When a third metal material is connected to a thermocouple circuit, as long as the temperature of the two contacts of the material is the same, the thermoelectric potential generated by the thermocouple will remain unchanged and will not be affected by the connection of the third metal to the circuit. Therefore, when using thermocouples for temperature measurement, a measuring instrument can be connected to measure the thermoelectric potential, and the temperature of the measured medium can be determined.
Vacuum gauge with charged particle effect
Hot Cathode Ionization Gauge
Hot cathode ionization gauge used for high-altitude measurement. When gas conducts electricity, gas molecules collide with high-speed flying electrons and ionize, and the frequency of the collision is related to the density of the gas molecules. The higher the density, the higher the frequency of collisions, and the more ions are produced; The density of gas molecules is directly related to the pressure of the gas. Therefore, if the size of the ionized ion flow in the gas can be measured, the pressure of the gas can be determined. This type of vacuum gauge is mainly used to measure high vacuum levels.
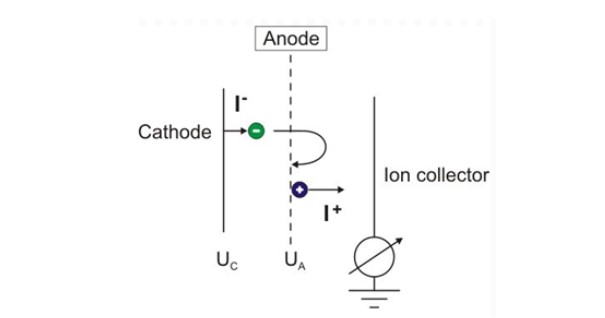
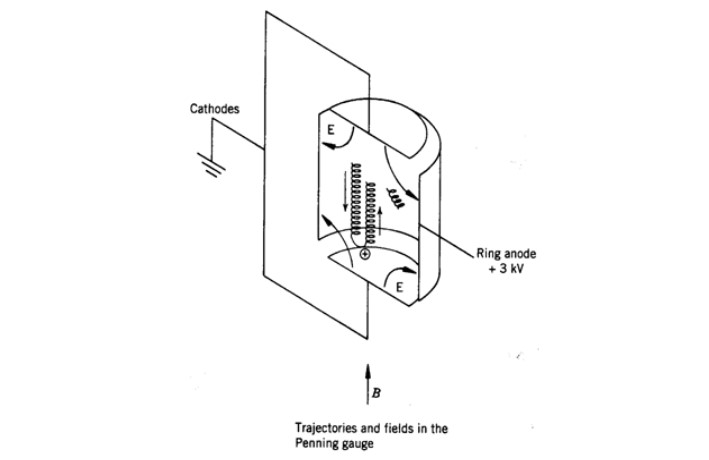
Cold Cathode Ionization Gauge
The cold cathode ionization vacuum gauge, like the hot cathode ionization vacuum gauge, utilizes the pressure dependent characteristics of ionization current of gas molecules under low pressure. The discharge current is used as the measurement of vacuum degree, which is indicated by an ammeter CB. The cold cathode ionization vacuum gauge relies on a small amount of initial free electrons generated by cold emission (field emission, photoelectric emission, gas ionization by cosmic rays, etc.), which move towards the anode under the action of an electric field. However, due to the presence of an orthogonal magnetic field, force is also applied to the moving electrons, thereby changing their motion trajectory.
In vacuum technology, cold cathode ionization vacuum gauge is an important tool for measuring vacuum degree, which can accurately measure high, medium, and low vacuum degrees. In electronic device manufacturing, cold cathode ionization vacuum gauge is used to monitor the vacuum degree during the process and ensure product quality. In the field of surface treatment, cold cathode ionization vacuum gauge is used to study the influence of surface treatment process on material properties and improve product performance.
Different types of vacuum gauges have their own advantages in different application scenarios. There are many types of vacuum gauges used as vacuum measurement devices, with different sensitivities, ranges, and applications. Commonly used ones include thermocouple vacuum gauges, Pirani (resistance) vacuum gauges, thin-film capacitance vacuum gauges, Bourdon vacuum gauges, cold cathode ionization vacuum gauges, and hot cathode ionization vacuum gauges. Specifically, the first three are used for low to medium vacuum measurements, while the latter three are suitable for high vacuum measurements. A general understanding of the different types and operating principles of vacuum gauges will help you choose the appropriate vacuum gauge according to your needs. If you are interested in or have any questions about specific types of vacuum gauges, you can click on the ATO Automation store to contact us!

