Stepper Motor Troubleshooting FAQs
Stepper motors are widely used in precision applications due to their accuracy and reliability. However, like any complex machinery, they can face issues that affect their performance. In this article, we'll explore common stepper motor problems and provide practical troubleshooting tips to help you keep your systems running smoothly.
1. How to Control Stepper Motor Direction?
Controlling the direction of a stepper motor is simple. For a two-phase motor, you can reverse the direction by swapping the connections of one of the phases. For example, exchange A+ with A-. For a three-phase motor, swap the wires of adjacent phases, such as U and V. This will reverse the motor’s rotation direction.
2. How to Address Vibration and Noise?
Excessive vibration and noise are often symptoms of the motor operating in an oscillation zone. To address this issue, try the following:
- Adjust the input signal frequency (CP) to avoid the oscillation range.
- Use a microstepping driver to reduce the step angle, resulting in smoother motor operation.
These steps will reduce the vibrations and make the motor run more quietly.
3. How to Troubleshoot Non-Operating Stepper Motors?
If your stepper motor doesn’t start after powering up, there could be several reasons:
- Overload Stalling: This can occur if the motor is overloaded, often accompanied by a whining noise.
- Motor in Offline State: Check if the motor is disconnected or in an offline mode.
- Signal or Wiring Issues: Ensure the control system is sending pulse signals to the driver and check for any wiring problems.

4. How to Resolve Motor Jerking and Interruptions?
If the motor is jerking or unable to run continuously, check for these common causes:
- Incorrect wiring: Ensure the windings are correctly connected to the driver.
- High Pulse Frequency: Check if the input pulse frequency is too high. Also, verify that the acceleration and deceleration settings are properly configured.
5. When to Utilize Offline Signals in Hybrid Stepper Motor Drivers?
The FREE signal in hybrid stepper motor drivers is used to disengage the motor when necessary. When the FREE signal is set to a low level, the driver cuts off the current to the motor, allowing the rotor to rotate freely. This feature is useful when manual operation or adjustments are required. Once the adjustments are done, reset the FREE signal to a high level to resume automatic control.
6. How to Select Power Supply Voltage and Current for Stepper Motor Drivers?
Choosing the correct power supply for your industrial stepper motor driver involves:
- Determining the required voltage and working current for the driver.
- Selecting power supply current: For linear power supplies, the current should be about 1.1 to 1.3 times the output phase current (I). For switching power supplies, the current should range from 1.5 to 2 times I for optimal performance.
By matching these values, you’ll ensure efficient operation and prevent overloading.
7. How to Optimize Power Supply Voltage for Stepper Motor Drivers?
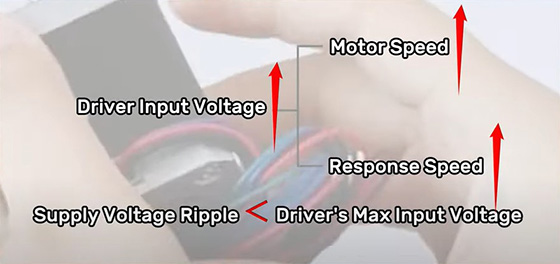
Stepper motor drivers accept a wide range of input voltages, selected based on the motor's operating speed and response demands. Higher speeds or faster responses necessitate higher voltages, but ensure that the power supply voltage ripple remains within the driver's maximum input voltage to prevent damage. Lower voltages can promote smoother motor operation and reduce vibration.
8. What is the Link Between Microstepping and Resolution?
Microstepping (or subdivision) is used to improve stepper motor resolution and reduce low-frequency vibrations. For example, in a two-phase hybrid stepper motor with a 1.8° step angle, if the subdivision driver is set to 4, the motor resolution will be 0.45° per pulse.
However, resolution isn't solely determined by microstepping. The precision of motor movement also depends on the current control accuracy of the microstepping driver. Different manufacturers may offer varying levels of precision, and higher microstepping values can make it more challenging to maintain accuracy.
9. Why Does the Torque Decrease with Increasing Speed in Stepper Motors?
The torque of a stepper motor decreases with higher speeds due to the back electromotive force generated by the motor windings' inductance. As the frequency increases, the counter electromotive force grows, leading to a reduction in phase current and subsequently diminishing torque output.
As we wrap up our discussion on the FAQs of stepper motor troubleshooting, remember that proactive maintenance, accurate configuration, and attentive diagnostics are essential for optimizing stepper motor performance and longevity. You can visit ato.com to purchase the stepper motor and stepper motor driver you need. If you have any questions, you can watch the video below to further understand.

