Residual Current Circuit Breaker Working Principle
In the field of electrical safety, the working principle of residual current circuit breaker is crucial. It is a safety device specifically designed to protect people from the dangers of electrocution and prevent electrical fires. At ATO store, we are committed to providing the most reliable residual current circuit breakers to ensure the safety of every customer. And understanding the working principle of residual current circuit breakers can better help you choose and use them properly. In this blog post, we'll take an in-depth look at how residual current circuit breakers work.
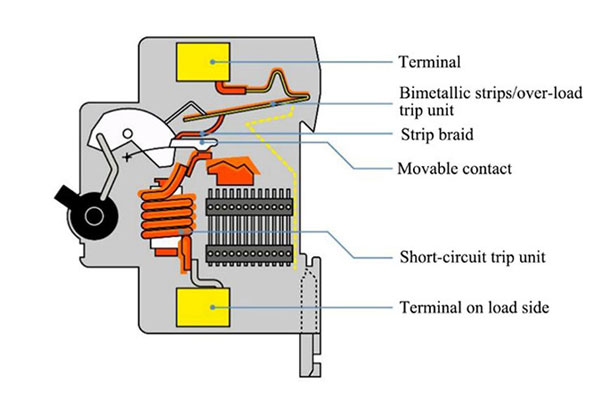
The Core Components of the Residual Current Circuit Breaker
Zero Sequence Current Transformer: Zero sequence current transformer is one of the core components of the residual current circuit breaker. Its role is to detect the leakage current in the circuit. Zero sequence current transformer is usually composed of a ring-shaped core and winding, the power supply line (fire and zero line) through the transformer's magnetic ring, forming a closed magnetic circuit. When there is no leakage current in the circuit, the magnetic flux in the iron core is zero; when there is leakage current, magnetic flux is generated in the iron core, and the zero sequence current transformer generates an induced voltage to drive the subsequent circuit, thus inducing an electromotive force in the winding. The size of this electromotive force is proportional to the size of the leakage current.
Electronic Control Circuit: Responsible for processing the zero-sequence current transformer induced voltage signal, and convert it into a switching signal. This part of the circuit includes amplifier circuit, filter circuit, comparison circuit, etc., used for the induction voltage signal amplification, filtering and comparison, in order to determine whether there is leakage phenomenon.
Leakage Detection Element: Leakage detection element is the executive part of the residual current circuit breaker, according to the signal output from the zero sequence current transformer, to determine whether a leakage fault occurs, and cut off the power supply when the leakage is detected. Common leakage detection element has electronic and electromagnetic two kinds. Electronic leakage detection components usually use semiconductor switching devices (such as thyristors, transistors, etc.) as a switching element, with high precision, fast response speed and other advantages; electromagnetic leakage detection components use the principle of electromagnetic induction, through the solenoid suction or release to realize the power supply on and off structure is simple, high reliability.
Test Button and Reset Button: Test button is used to regularly test the residual current circuit breaker working status is normal; reset button is used to restore its normal working status after the residual current circuit breaker action. These two buttons are usually set on the housing of the residual current circuit breaker, which is convenient for users to operate.
In addition, the residual current circuit breaker may also include other auxiliary components, such as housing and terminals, operating mechanism (handle, locking, jumping buckle, lever), etc., these components work together to ensure that the residual current circuit breaker's normal operation and safety of use.
Residual Current Circuit Breaker Working Principle
Residual current circuit breaker working principle is based on Kirchhoff's current law, i.e. at any node, the current flowing into the node is equal to the current flowing out of the node. Under normal conditions, the sum of the currents in the phase, neutral and ground wires should be zero. When a leakage occurs, some of the current will flow back to the power supply through the ground, resulting in a non-zero zero sequence current. The residual current circuit breaker determines whether leakage occurs in the circuit by detecting the zero sequence current. Specifically, the working principle of the residual current circuit breaker (RCCB) can be divided into the following steps.
The Zero Sequence Current Transformer Detects the Zero Sequence Current: when the residual current circuit breaker is in normal operation, the current in the circuit flows from the fire line of the power supply to the load, and then flows back from the load. The magnetic flux generated by the currents on the fire and zero lines of the power supply cancel each other out so that no voltage is induced on the secondary coil. This means that for a three-phase circuit, the sum of the currents in the three phase and neutral wires should equal zero. A residual current circuit breaker uses a zero sequence current transformer to monitor the current vector sum in the main circuit. In this case, the zero sequence current transformer in the residual current circuit breaker detects a current vector sum of zero. The residual current circuit breaker is closed and the circuit is normally powered.
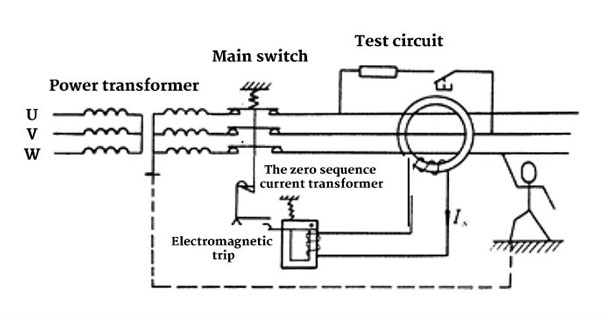
However, when a leakage fault occurs in the circuit, there is a leakage in the circuit or a line is not connected to the zero line, a part of the current will flow into the residual current circuit breaker point instead of all of it flowing back to the zero line of the power supply. At this point, the current in the fire line and the zero line will be unbalanced, which results in the current vector sum detected by the zero sequence current transformer is no longer zero. Once the current difference reaches the set value of the residual current circuit breaker, the zero sequence current transformer transmits this non-zero zero sequence current signal to the earth leakage trip detector. The magnetic flux in the magnetic ring changes and a voltage is induced on the secondary coil. This induced voltage will pass through the electromagnet to make the tripper actuate.
Leakage Detector Action: The leakage detector receives the signal from the zero sequence current transformer, and judges that there is a leakage in the circuit. At this time, the leakage detector will act to trip the circuit breaker, thus cutting off the power supply.
The Operating Mechanism Controls the Circuit Breaker to Trip: The operating mechanism receives the action signal of the earth leakage tripper, and then controls the circuit breaker to trip. After the circuit breaker trips, the power supply is cut off, thus protecting personal safety and equipment from damage.
Auxiliary Contacts to Realize Remote Control and Signal Transmission: Auxiliary contacts can be used to realize remote control and signal transmission. For example, when the residual current circuit breaker trips, the auxiliary contact can send out a signal to notify the monitoring system or the operator to handle.
As an important electrical protection device, the residual current circuit breaker plays a vital role in safeguarding our electrical safety. By understanding the working principle and core components of the residual current circuit breakers, we can better use and maintain residual current circuit breakers to ensure that they are always in good working condition. In daily life and industrial production, we should attach great importance to the safety of electricity, the correct selection, installation and use of the residual current circuit breakers.

