Power Divider vs. Power Splitter
Power divider is a key component in RF (Radio Frequency) systems designed for high-power applications. This device serves as both a power combiner and a splitter, effectively splitting the input RF signal into multiple paths or combining signals from different sources. Although the three-resistor power divider and the two-resistor power divider are similar components, they have different characteristics. Therefore, both have the most suitable and different use cases, which means they are not interchangeable. Although they look very similar, their functions and application scenarios are vastly different. This article will explore the differences between these two allocators.
Different Working Pricinples
The biggest difference between power dividers and power splitters is the configuration of the resistors. If you take a look at the circuit diagrams below, you can spot this fundamental difference for yourself.
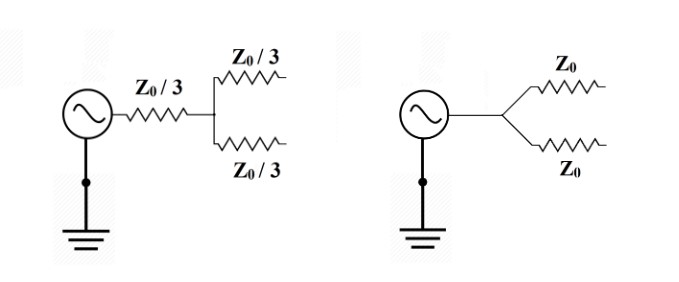
The power divider (on the left) uses three resistors to divide power. This is great for applications where one power source must split and fed to different components to ensure phase coherence. On the other hand, The power splitter (on the right) utilize a two-resistor configuration which makes them the ideal choice for leveling and ratio measurements. Furthermore, when used in reverse, a power splitter can effectively be used as a power combiner.
Different Applications
The power divider is commonly used for testing and measuring systems. Another point is that the power divider can also be used as a power combiner. For example, a three-resistor power divider can be used to distribute signals to two different antennas. Power dividers can also be used to perform intermodulation distortion (IMD) measurements. In this case, the power divider is actually used as a power combiner. Two signals from two different sources are combined and then applied to the device under test (DUT). Spectrum analyzer is used to measure the output of DUT. In addition, diversity gain measurement represents another application area of power dividers.
The dual resistor power divider can be used for gain and power testing. This document shows a block diagram of an amplifier test setup using a power divider. As mentioned earlier, leveling or ratio is another use case for power dividers. Two diagrams are provided to illustrate the leveling application. The first one consists of a power divider and a crystal detector. The second method is to use a power meter instead of a crystal detector.This component can be used for leveling ring measurement applications. Using a dual resistor power divider for source balancing can effectively improve source matching.
Different Structures
A three-resistor voltage divider is composed of three 16 2/3 Ω resistors. Power divider is used to divide signals into two equal parts for comparative measurement. The power divider can provide good impedance matching at both output ports. It can also be used to measure different properties of two output signals, such as frequency and power. Power dividers can also be used for combining two signals, as these ports are bidirectional.
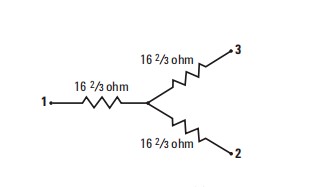
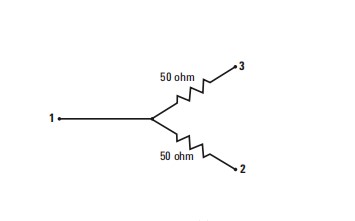
A dual resistor power divider is composed of two 50 Ω resistors. The Power spliter also divides power into two equal parts. Unlike the power divider, which has three built-in 16.7ohm resistors, it has two built-in 50ohm resistors. The power spliter only matches the input port to 50 ohms, and the impedance of the two output ports is 83.33 ohms. This way, the output port can achieve VSWR=1:1 matching. So, a power splitter can be called a power splitter, used to improve the matching between output and source in level and ratio measurements, thereby minimizing measurement uncertainty.
Different Advantages
A power divider is an RF microwave accessory with an equivalent 50ohm resistor per port. These accessories evenly distribute the power of the transmission line between ports to achieve comparative measurements. When the input terminates at the system characteristic impedance (50 Ω), the power divider provides good impedance matching at both output ports. Once good source matching is achieved, a power divider is used to divide the output into equal signals for comparative measurement. Power dividers can also be used in testing systems to measure two different characteristics of signals, such as frequency and power, for broadband independent signal sampling. In addition to dividing power, it can also serve as a power combiner because they are bidirectional.
A power splitter allows you to increase the number of outlets available for use. This is particularly useful when you have limited power outlets in a room or when you need to connect multiple devices in close proximity. Power splitters help to save space by eliminating the need for multiple power adapters and cords. This is especially beneficial in compact spaces or when you have limited desk or floor space. Some power splitters come with built-in surge protection, which helps to safeguard your devices against power surges and voltage spikes. This can be particularly important when you have sensitive electronic equipment that needs to be protected.
In short, when you want to purchase power dividers, you can choose based on their different structures, application scenarios, and advantages, and try to choose the one that meets your needs as much as possible. If you have any questions, you can always send a message through ATO Industrial Automation store to inquire.

