Pneumatic Valve Actuator Working Principle
Pneumatic valve actuators are actuators that use air pressure to drive open, close or adjust valves. Pneumatic actuators are sometimes equipped with certain auxiliary devices, commonly used are valve positioners and handwheel mechanisms. The function of the valve positioner is to use the feedback principle to improve the performance of the actuator, so that the actuator can achieve accurate positioning according to the control signal of the controller. The function of the handwheel mechanism is to use it to directly control the control valve to maintain normal production when the control system is powered off, gas out, the controller has no output or the actuator fails. Next, we will show you how does the pneumatic valve actuator work.
Double acting pneumatic actuator working principle

When the air source pressure enters the middle cavity between the two pistons of the cylinder from the air port (2), the two pistons are separated and moved toward both ends of the cylinder, the air in the air cavities at both ends is discharged through the air port (4), and the two piston racks are synchronized Drive the output shaft (gear) to rotate counterclockwise. On the contrary, when the air source pressure enters the air chambers at both ends of the cylinder from the air port (4), the two pistons move toward the middle of the cylinder, the air in the middle air chamber is discharged through the air port (2), and the two piston racks simultaneously drive the output shaft (gear). ) rotate clockwise. If the piston is installed in the opposite direction, the output shaft will rotate in the opposite direction.
Single acting pneumatic actuator working principle
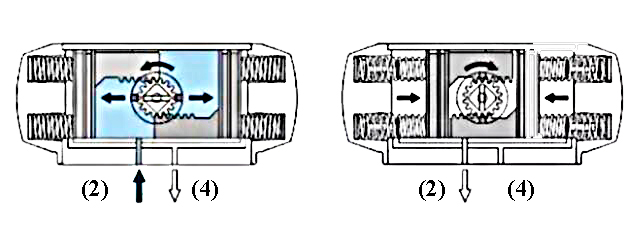
When the air source pressure enters the middle cavity between the two pistons of the cylinder from the air port (2), the two pistons are separated and moved toward both ends of the cylinder, forcing the springs at both ends to compress, and the air in the air cavities at both ends is discharged through the air port (4), and at the same time The two piston racks are synchronously driven to rotate the output shaft (gear) counterclockwise. After the air source pressure is reversed by the solenoid valve, the two pistons of the cylinder move in the middle direction under the elastic force of the spring, the air in the middle air cavity is discharged from the air port (2), and the two piston racks simultaneously drive the output shaft (gear). Rotate clockwise. If the piston is installed in the opposite direction, the output shaft will rotate in the opposite direction when the spring returns.

