Inductive Proximity Sensor vs. Magnetic Proximity Sensor
Inductive sensors and magnetic sensors are both types of sensors that can detect the presence or proximity of objects without physical contact, but they work in different ways and have different strengths and weaknesses.

Difference Between Inductive and Magnetic Proximity Sensor
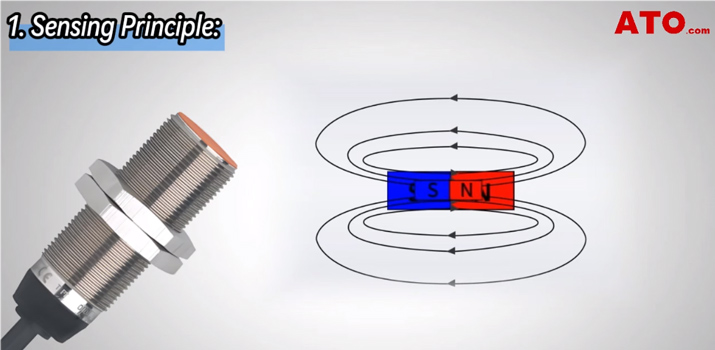
1. Sensing Principle
Inductive proximity sensors use electromagnetic fields to detect the presence of metallic objects. Whenever a metallic target comes within its sensing range, it causes a shift in the field and activates the sensor. When the target moves away from the sensor to or beyond the ‘inactive' point, the sensor switches off. Magnetic proximity sensors, on the other hand, detect objects based on changes in magnetic fields. When a magnetic object enters the sensor's range, it alters the magnetic field, triggering the sensing process.
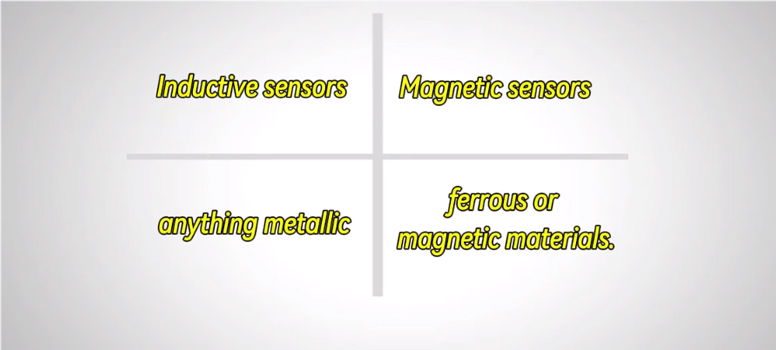
2. Material Sensitivity
As we all know, different proximity sensors can detect various objects in different ways. Inductive proximity sensors are primarily designed to detect ferrous and non-ferrous metals such as iron, aluminum, brass and copper. However, their sensing range may change based on the type of metal being detected. By contrast, magnetic sensors are specifically designed to detect objects that possess magnetic properties, like permanent magnets. The difference between the two types is that the inductive prox sensors will trigger on anything metallic, while magnetic sensors will only trigger in the presence of ferrous or magnetic materials.
3. Sensing Range
Another key difference between inductive and magnetic sensors is their range. The operating distance of the sensor is strictly linked to the nature of the material. In general, inductive proximity sensors tend to have shorter operating distances compared to magnetic proximity sensors. And they provide some correction factors in their datasheet when you want to detect non-ferrous metal targets. Compared with inductive types proximity sensors, magnetic sensors typically have a longer detection range, maxing out to 80mm.
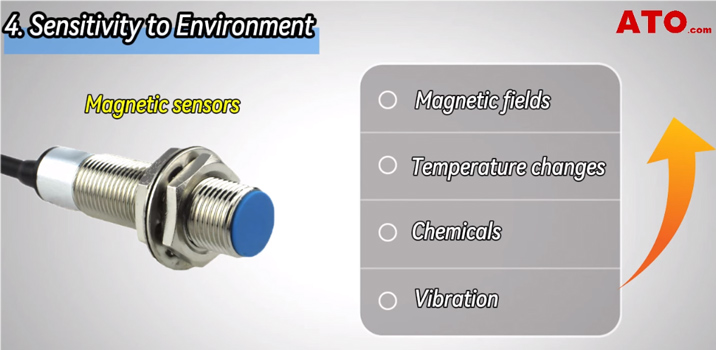
4. Sensitivity to Environment
These two types of sensors are also different in their sensitivity to environmental conditions. Magnetic sensors can be affected by external conditions such as other magnetic fields, severe temperature changes, chemicals and and physically unstable harsh environments (vibration), while inductive sensors are less affected by these factors.
Pros and Cons of Inductive and Magnetic Sensors
Following that, we've summarized the advantages and disadvantages of these two sensing technologies. Using inductive sensors has the following advantages over magnetic sensors:
The inductive proximity sensor is powerful and versatile in metal sensing. They can detect metal targets through non-metallic barriers. They also have high switching rates for fast response to objects in counting applications. In addition, they are not affected by dirty, greasy, harsh environmental conditions and have excellent environmental adaptability. Inductive proximity sensors are solid-state with no moving parts, ensuring a longer service life.
As to their disadvantages or limitations of, inductive proximity sensors lack in detection range, averaging a max range of up to 60 mm. Although they're capable of metal sensing, inductive sensors are limited to detecting metal objects, and using non-ferrous materials decreases their operating distance.
In contrast to the inductive type, magnetic sensors feature the following advantages.
- Firstly, magnetic prox sensors do not require an active supply to operate, thus simplifying their design, reducing overall cost and minimizing power consumption in practical applications.
- Secondly, magnetic sensors can operate freely through plastic and non-ferrous materials, allowing for sensing even across hermetic barriers.
- Thirdly, they aren't affected by dust, dirt, oil or other contaminants that can damage other types of sensors, making them capable in harsh environments.
And besides, they also have a fast response time in the detection of magnetic materials. Magnetic prox sensors also have their own limitations. They are not suitable for directly detecting non-metallic materials that lack magnetic properties. And they can be detrimentally influenced by external ferromagnetic interference. This sensitivity to other present magnetic fields can spoil measurement accuracy.
To sum up, the inductive proximity sensor is the go-to option for detecting metallic targets considering their versatility, high switching rate and anti-interference performance, while magnetic proximity sensors beat out the competition in terms of energy efficiency, anti-blocking capability and adaptability in harsh environments.
Applications of Inductive and Magnetic Proximity Sensors
Now that we understand the differences, let's explore their applications. Inductive proximity sensors are widely used in applications where metallic objects need to be detected, such as security-related applications, and their high switching speeds make them popular for automation applications such as product counting or sorting on assembly lines for the automotive industry.
On the other hand, magnetic proximity sensors find applications in areas such as security systems, door and gate automation, and position sensing, where the detection of magnetic objects is desired.
Overall, the choice between inductive and magnetic sensors depends on the specific application and the type of material being detected. To learn more about these sensors, see the table below.
| Types | Inductive Sensor | Magnetic Sensor |
| Principle | It uses current induced by magnetic fields to detect nearby metal objects | Based on a mechanical principle the magnetic field |
| Material detected | Metallic only | Magnet |
| Operating distance | Low: <50mm | Medium:<80mm |
| Robustness to vibration | High | Hall-effect: High Reed-techno: Low |
| Cost | Low | Low |
| Sensitivity | Any | Hall effect-sensitive EMC Reed techno-magnetic field disturbances |
| Applications | 1. Machine tools, assembly line, automotive industry 2. Detection of metal parts in harsh environments 3. High-speed moving parts |
1. Object detection 2. Position Monitoring of Moving Surfaces (e.g. a door, window, gate, etc.) |
If there is anything you don’t understand in this blog, you can refer to the video below. Also, welcome to ATO Automation Store to learn more about types of proximity sensors.



