How to Size Capacitors for 3-Phase Generator Conversion?
When converting a three-phase induction motor into a generator, correctly sizing the capacitors is crucial to ensure efficient operation. Capacitors are used to offset the inductive characteristics of the motor, improving its power factor and overall efficiency. If you're wondering, “What size capacitor should I use?”, this guide will walk you through the process of determining the correct capacitor size for your generator conversion project. In this tutorial, ATO industrial automation will explain what ‘capacitor size’ implies and provide you with all necessary formulas and important considerations you would need to figure it out yourself.
What is Capacitance?
Capacitance is a measure of a capacitor's ability to store charge when a voltage is applied across it. This fundamental property is crucial when converting a motor to a generator because it directly impacts the motor's performance and efficiency. The capacitor compensates for the motor’s inductive reactance, thereby improving the power factor and reducing energy losses.
Key Parameters for Capacitor Sizing
- Several factors influence the size of the capacitor you need. Here's a breakdown of the most important parameters to consider:
- Motor Power Rating: The power rating (in horsepower or kilowatts) of the motor will determine the capacitance needed. A higher power rating generally requires a larger capacitor.
- Capacitor Voltage Rating: This refers to the maximum voltage a capacitor can withstand. Always choose a capacitor with a voltage rating higher than the line voltage to ensure safety.
- Motor Power Factor: Power factor is the ratio between active power (watts) and apparent power (volt-amperes). It indicates the efficiency with which the motor uses electricity. For most induction motors, the power factor is typically assumed to be 0.8.
- Motor Full-Load Current: The current the motor draws at full load helps in calculating the apparent power.
- Desired Generator Speed (RPM): The speed at which the generator operates will affect the sizing of the capacitor.
Capacitor Sizing Formulas
To determine the correct capacitor size, you need to perform several calculations. The necessary capacitance value is based on the motor's power rating, voltage, power factor, and other parameters. Here are the basic formulas used for sizing the capacitor:
- Calculate apparent power (kVA): kVA = (HP * 746) / (Voltage * Power Factor)
- Calculate reactive power (kVAR): kVAR = kVA * sin(arccos(Power Factor))
- Calculate capacitance per phase (uF): C = (kVAR * 10^6) / (2 * π * Frequency * Voltage^2)
Where:
- C is capacitance in microfarads (uF)
- π = 3.14159
- Frequency is the AC line frequency (Hz)
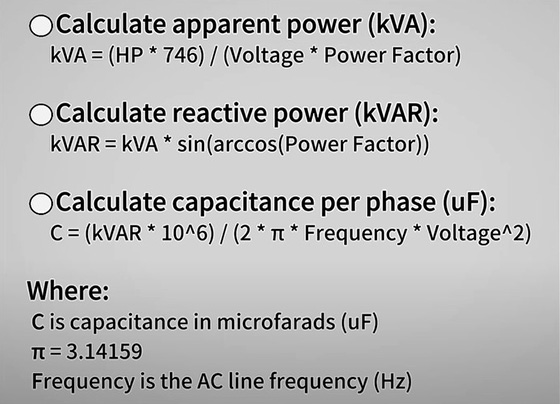
Here is a brief description of each of the above equations:
First you need to calculate the apparent power based on the input values of the motor’s horsepower, voltage, and power factor. Next, determine the reactive power by multiplying the apparent power (kVA) by the sine of the arccosine of the power factor. Finally, calculate the capacitance per phase in microfarads (uF) required. These calculations are essential in ensuring the capacitor is sized correctly for the generator conversion. For a clearer understanding, here is an example of the step-by-step calculation procedures to determine the desired capacitor size based on the provided equations.
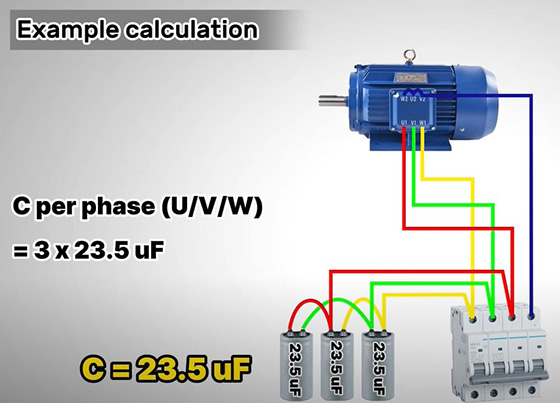
Example calculation
Suppose we have a 5 HP, 208V, 3-phase induction motor to be converted to a generator, with a desired operating speed and power factor of 0.8.
Firstly, enter the horsepower, voltage and power factor of the motor into the first formula to gain the apparent power. The result is 22.5 kVA. Secondly, figure out the reactive power by multiplying the calculated apparent power by the sine of the arccosine of the power factor 0.8, which is 0.6. The reactive power is calculated as 15.7 kVAR. Lastly, assuming the AC line frequency is 60Hz, multiply 15.7 kVAR by 10^6, and then divide the result by the product of 2, π (approximately 3.14159), 60 representing the line frequency, and 208 squared. The result, approximately 23.5 microfarads (μF), signifies the capacitance needed for your electric motor. Here are the steps:
- Calculate kVA: kVA = (5 HP * 746) / (208V * 0.8) = 22.5 kVA
- Calculate kVAR: kVAR = 22.5 kVA * sin(arccos(0.8)) = 15.7 kVAR
- Calculate capacitance per phase (assuming a 60Hz line): C = (15.7 kVAR * 10^6) / (2 * π * 60 * 208^2) = ~ 23.5 uF
The resulting microfarad should match the size of each capacitor, but the total capacitance per phase is 3 times the individual capacitor value as in our 3-phase generator system, the capacitor bank is connected in parallel in a star scheme. And that is so much about the calculation part.
Other Considerations
Apart from the above parameters, other things to consider when deciding what size capacitor to use for your 3-phase motor are factors such as frequency, ripple current rating, temperature and the physical size of a capacitor. And the motor’s design and intended application affect the optimal capacitor size. So please refer to motor nameplate or consult the motor manufacturer's specifications if available.
Sizing capacitors for a 3-phase motor-to-generator conversion requires careful calculations based on the motor's power rating, voltage, power factor, and other parameters. By following the formulas and guidelines provided, you can select the correct capacitor size to ensure your generator operates efficiently. Always consult motor specifications and capacitor ratings to make sure you're using the appropriate components for your specific application. With the right capacitor bank in place, you can effectively convert a motor into a reliable, low-cost generator. If you have any questions, you can watch the video below to further understand.

