Pneumatic Cylinders
Double Acting Pneumatic Cylinder, 100mm Bore, 50mm Stroke
Double Acting Pneumatic Cylinder, 25mm Bore, 75mm Stroke
Single Acting Pneumatic Cylinder, 20mm Bore, 75mm Stroke
Rodless Air Cylinder, 25mm Bore, 300mm Stroke, Double Acting
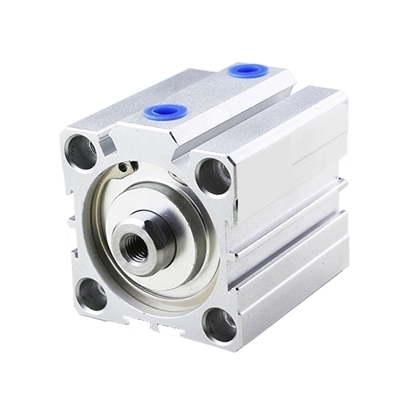
Compact Pneumatic Cylinder, 100mm Bore, 100mm Stroke, Double acting
Double Rod Cylinder, 40mm Bore, 300mm Stroke, Double Acting
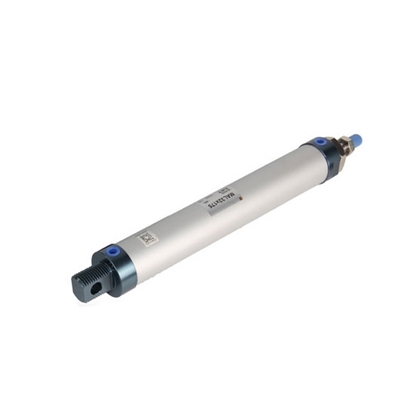
Small Pneumatic Cylinder, 20mm Bore, 300mm Stroke
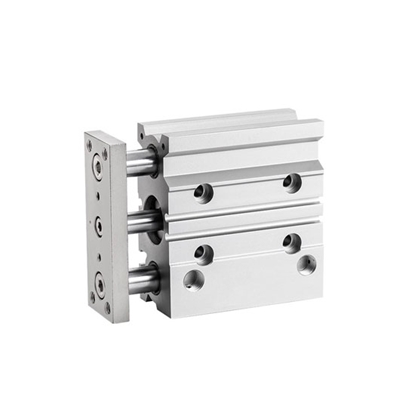
Guided Pneumatic Cylinder, Double Acting, 12mm Bore, 250mm Stroke
Guided Pneumatic Cylinder, Single Rod, 40mm Bore, 25mm Stroke
10mm Rotary Pneumatic Cylinder, Vane Type
40mm Rotary Pneumatic Cylinder, Vane Type
Mini Needle Cylinder, Single Acting
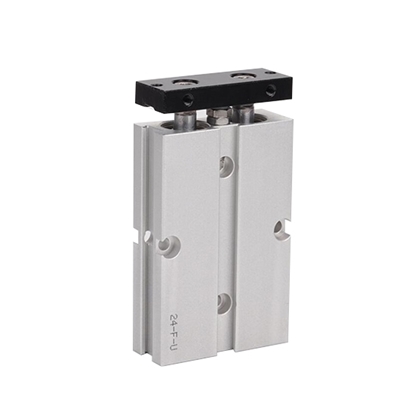
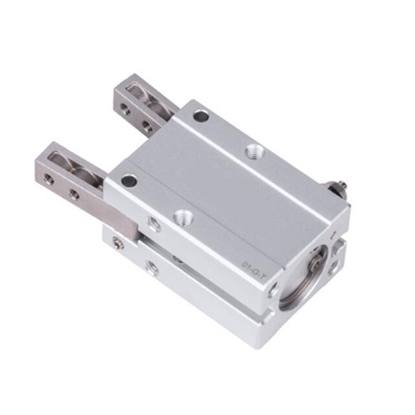
Pneumatic Slide Cylinder, 16mm Bore, 25mm Stroke
Pneumatic Slide Cylinder, 20mm Bore, 100mm Stroke
2 Finger Type Gripper Cylinder
3 Finger Type Gripper Cylinder
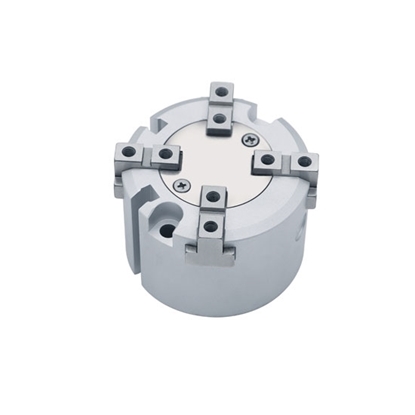
4 Finger Type Gripper Cylinder
6mm-32mm Bore Size Pneumatic Gripper, Double Acting
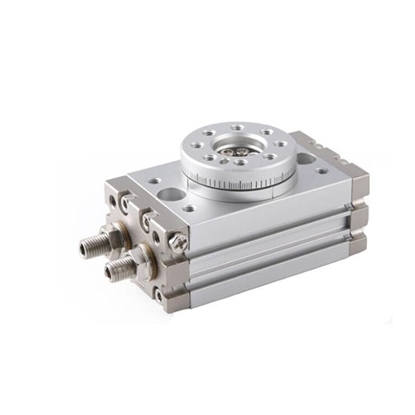
Pneumatic Rotary Actuator, Rack and Pinion, Double acting
Pneumatic cylinders (also known as air cylinders) are a type of compressed air-actuated device whose operating fluid is a gas producing a force acting on a piston inside a cylinder to extend and retract the piston in a reciprocating linear motion. For all other numerous types of pneumatic cylinder varying in appearance, size and function, they generally fall into one of the two specific categories, double acting and single acting. ATO offers heavy-duty and space-saving pneumatic cylinders manufactured with high quality, corrosion-resistant material and available in the extensive selection of sizes, strokes and functions. With trusted capabilities and performance, we supply through fast and free shipping multi-type products such as standard and compact pneumatic cylinders, rodless air cylinders, pneumatic grippers, double rod cylinders, pneumatic rotary cylinders and much more to complete your pneumatic control system.
Types of pneumatic cylinders
Classification by structural features of pneumatic cylinders
- Piston type pneumatic cylinder which includes: common single pneumatic acting cylinder, common double acting cylinder, double piston rod cylinder, differential cylinder, multi-bit cylinder, tandem cylinder, impact cylinder, rodless cylinder, magnetic piston cylinder, stepper cylinder, booster cylinder, pneumatic-hydraulic booster cylinder, oil damping cylinder, rack and pinion drive cylinder, cable cylinder, special cylinder, etc.
- Membrane pneumatic cylinder which includes: single acting membrane cylinder, double acting membrane cylinder.
- Oscillating (or vane type) cylinder which includes: single vane oscillating pneumatic cylinder, double vane oscillating pneumatic cylinder.
Pneumatic cylinders are classified according to the installation form
- Fixed cylinder (installed in the body fixed): lug type, flange type, flange type, rodless cylinder.
- Shaft pin cylinder (cylinder body around the fixed axis for the angle of swing): head, tail shaft pin type, middle shaft pin type cylinder, rotating (piston rod and machine tool spindle connection with air sleeve immobile) cylinder.
- Rotary pneumatic cylinder
- Embedded pneumatic cylinder
Category according to the function type of pneumatic cylinder
- Conventional pneumatic cylinder
- Buffer type pneumatic cylinder
- Rotary pneumatic cylinder
- Swing pneumatic cylinder
- Pneumatic cylinder with gas-hydraulic damping
- Shock pneumatic cylinder
- Step pneumatic cylinder
- Special pneumatic cylinder
Pneumatic Cylinder Working Principle
A pneumatic cylinder is a cylindrical metal machine that guides a piston in a straight-line reciprocating movement in a cylinder. The air converts heat energy into mechanical energy through expansion in the engine cylinder, and the gas receives piston compression in the compressor cylinder to increase the pressure.
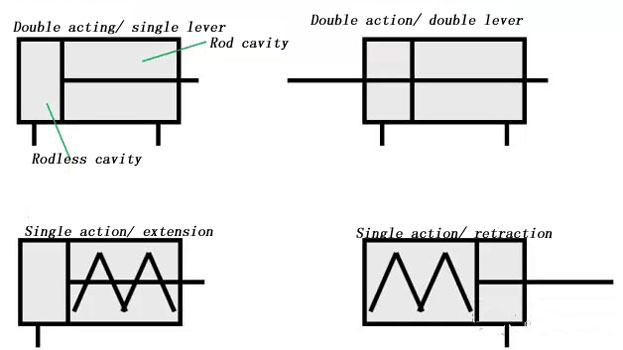
Cylinder retracts

Cylinder protrusion

When the compressed air is input from the rodless cavity, there is a rod-cavity exhaust, the pressure difference between the two Chambers of the cylinder ACTS on the piston to push the piston movement, so that the piston rod extends. When there is a rod-cavity air intake, no rod-cavity exhaust, make the piston rod retraction, if there is a rod-cavity and rod-cavity alternate air intake and exhaust, the piston reciprocating linear movement.
How to choose the size of the pneumatic cylinder?
The diameter of the cylinder piston rod is very important. A more common mistake in cylinder design can be an undersized piston rod, making the cylinder more susceptible to stress, wear and failure. Piston rod diameters can range from 0.5 inches to over 20 inches, but they must be sized for the available load. In pushing applications, it is important to correctly size the rod diameter according to Euler calculations to avoid rod buckling or bending. When designing a cylinder to generate the required force, the size of the cylinder rod is always the primary consideration.
Prevent the rod from bending. In a long-stroke cylinder, a fully extended rod can bend under its own weight. Excessive bending can cause wear and damage to seals and bearings. It can even cause the piston to cock up in the hole, scratching and damaging the inner surface of the cylinder. Rod deflection must not exceed 1 to 2 mm.
Cylinder rods that are at risk of bending or misalignment require additional support. Depending on the stroke length, a stop tube may be required; this increases the bearing area of the cylinder to prevent excessive wear. Engineers may also consider using larger diameter rods for added strength. But it also adds weight and can be self-defeating, so do the math.
When choosing the appropriate size, we also need to pay attention to the impact load of the cylinder. Stroke length, the distance required to push or pull a load, can range from less than an inch to several feet or more. But when the cylinder is extended or retracted, make sure the piston doesn't bottom out and create a shock load at the end of the stroke. Engineers have several options: add an internal cushion to slow the load near the end of the stroke; add an external mechanical stop to prevent the cylinder from bottoming out; or use proportional valve technology to precisely meter flow and safely slow the load.
12 Tips for Using a Pneumatic Cylinder
1. Pay attention to keeping the distance between parallel cylinders
The distance between the cylinders of the two parallel cylinders must be greater than 40mm, otherwise the magnetic switches of the two cylinders will interfere with each other and cause malfunction.
2. The magnetic switch wiring should be shortened as much as possible
The length of the wiring has no effect on the function usage, but if the wiring is too long, the current will be large when the switch is turned on, which will shorten the service life of the switch. If the wiring must be very long, more than 5 meters, you must use a contact protection box.
3. Precautions for use in special environments
- In the strong magnetic environment, use a switch cylinder with strong magnetic field resistance;
- When there is a lot of dust and there are water droplets or oil droplets, a telescopic protective cover should be used on the cylinder rod side;
- In an environment with iron powder and iron filings nearby, if there is no protection, the magnet will attract the iron powder and iron filings to gather around it, which will weaken the magnetic force in the cylinder, which may cause the magnetic switch to not operate.
4. Note that the shaft of the single-axis cylinder will rotate
Unless it is an anti-rotation single-axis cylinder, the shaft of the single-axis cylinder will rotate during movement, which may cause the bolted connection to the head of the piston rod to loosen.
5. The piston rod must not be subjected to radial force
The piston rod can only be subjected to the axial push-pull force. Don't feel that the rod is thick and strong and let it be subjected to lateral force. Once the lateral force is applied, the guide rod and the inner wall of the cylinder will have a different force, which will greatly shorten the service life of the cylinder.
If there is radial force, - be sure to add guide rods or slide rails to assist, or directly select the cylinder with slide rails and guide rods.
6. The cylinder action should be protected
Cylinders can easily hurt people, and large cylinder diameters can directly make people disabled or even die. If there is no safety grating on the outside of the machine, the place where the cylinder moves must be protected.
7. Additional buffering is important
When the mass of the driven object is large and the speed is fast, the buffer capacity of the cylinder itself is generally insufficient. We must add a hydraulic buffer or set a deceleration circuit to assist the deceleration and stop.
8. The cylinder of the guide rod can never be used as a gear point.
There is a special blocking cylinder for the gear point. Don't think that the cylinder with the guide rod can also be used as a gear point. It cannot withstand radial impact. Months, the guide rod will be loose, resulting in inaccurate positioning.
9. Design support in the middle of the long stroke cylinder
Support should be designed in the middle of the long stroke cylinder to overcome the sagging of the piston rod, the sagging of the cylinder barrel, and the damage caused by the vibration and external load of the piston rod.
10. Fully consider the influence of power failure and gas failure and cylinder malfunction
It is the gripper cylinder. When carrying things, the power is suddenly cut off or the air is cut off. If there are no protective measures, the goods to be carried may fall, smash the machine or damage the product.
If you want to prevent the cylinder from malfunctioning due to power failure, you can choose a double-coil solenoid valve, which can maintain the original action of the cylinder in the event of a power failure.
11. The piping between the cylinder and the solenoid valve is not too long
If the piping between the cylinder and the solenoid valve is too long, the gas will not be easily discharged and replaced, and it will be easy to condense after a long time.
12. Anti-loose in vibration occasions
If the cylinder is used in the occasion of high work and high vibration, attention should be paid to preventing loosening of the design, installation screws and various connection links.























